Your Cart
Your Cart is currently empty.
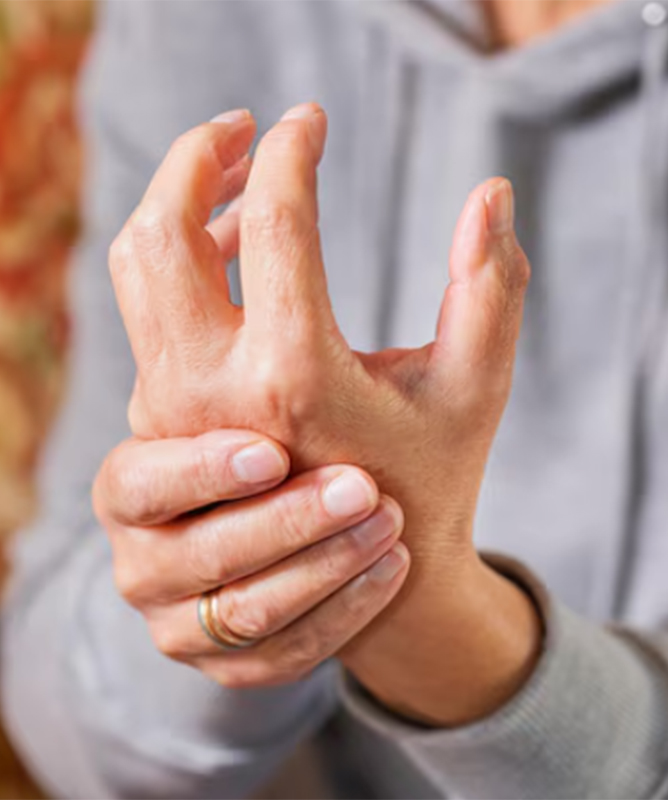

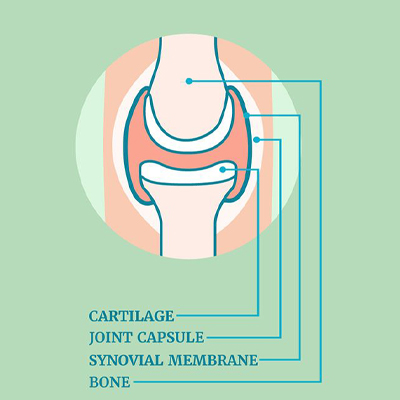
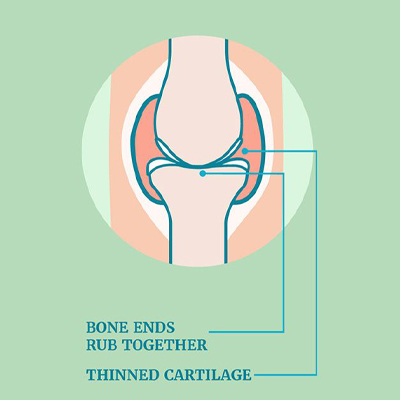
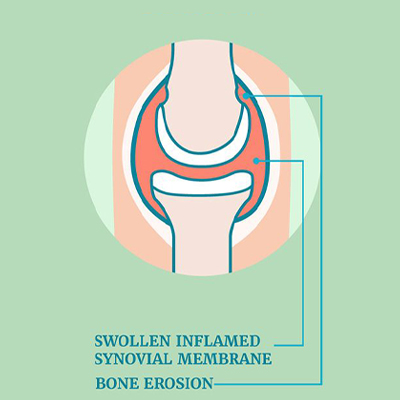
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition that causes inflammation, pain, and stiffness in the joints, muscles, and connective tissues. It primarily affects the joints, leading to swelling, pain, and reduced mobility, which can make daily activities difficult. Over time, RA can cause the breakdown of cartilage—the cushiony tissue that helps the joints move smoothly—leading to further joint discomfort as bones begin to rub together.
In Ayurveda, Rheumatic Arthritis is known as “Amavata,” where an accumulation of toxins (Ama) in the joints, combined with imbalances in the Vata dosha (air element), causes inflammation and pain.
Rheumatic Arthritis is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors:
Genetic Predisposition: Family history can increase your risk.
Autoimmune Reaction: The body mistakenly attacks its own tissues, leading to inflammation.
Environmental Triggers: Smoking is a significant risk factor, as well as infections and a poor diet.
Diet and Nutrition: Diets high in processed foods and low in fiber may increase risk, while omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation.
Hormonal Imbalances: RA is more common in women, especially in those aged 65-80.
Joint Pain and Swelling: Often affecting the knees, fingers, and wrists.

Stiffness: Particularly noticeable in the mornings or after periods of inactivity.

Fatigue: A common and often debilitating symptom.

Decreased Range of Motion: Limited movement in the affected joints.

Joint Pain and Swelling: Often affecting the knees, fingers, and wrists.

Stiffness: Particularly noticeable in the mornings or after periods of inactivity.

Fatigue: A common and often debilitating symptom.

Decreased Range of Motion: Limited movement in the affected joints.
– Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARD):
Limitations: Long-term use can lead to liver toxicity, bone marrow suppression, and gastrointestinal issues.
– Biologic Agents (TNF Inhibitors):
Limitations: High cost, increased risk of infections, and potential cancer risk with prolonged use.
– Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
Limitations: Long-term use can cause gastrointestinal issues, kidney damage, and increased cardiovascular risk.
Phone number:
+91 6379926961
Location:
429A, V.V.C Layout, Pulliyakulam Road, Coimbatore – 641018.
Email:
support@namashivayah.com
