Your Cart
Your Cart is currently empty.

Hair Loss and scalp problems are very common complaints from many patients to Dermatologists. Hair Loss can be categorized into many sub-sections and they can happen due to genetic conditions, hair pulling, stress, or due to the environment around. Any type of hair loss can cause distress in a person and can also lead to that person looking older than their actual age.
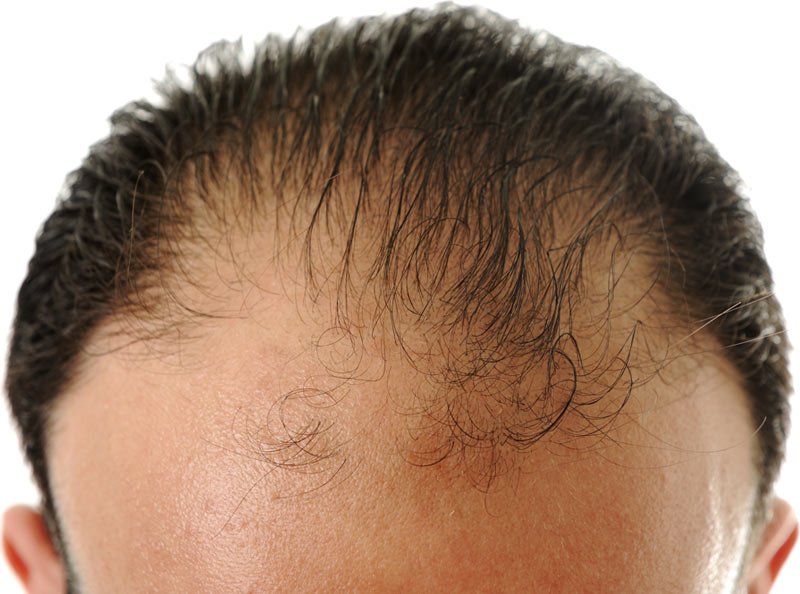
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male pattern baldness, is a genetic condition that predominantly affects men. It is characterized by a receding hairline and thinning of hair on the crown of the scalp. This type of hair loss is driven by hormonal factors and can start in the late teens or early adulthood.

Similar to male pattern baldness, female pattern baldness is a genetic form of hair loss affecting women. It typically causes a widening part and thinning of hair, especially on the crown area. Hormonal changes, aging, and genetic predisposition are contributing factors to this condition.
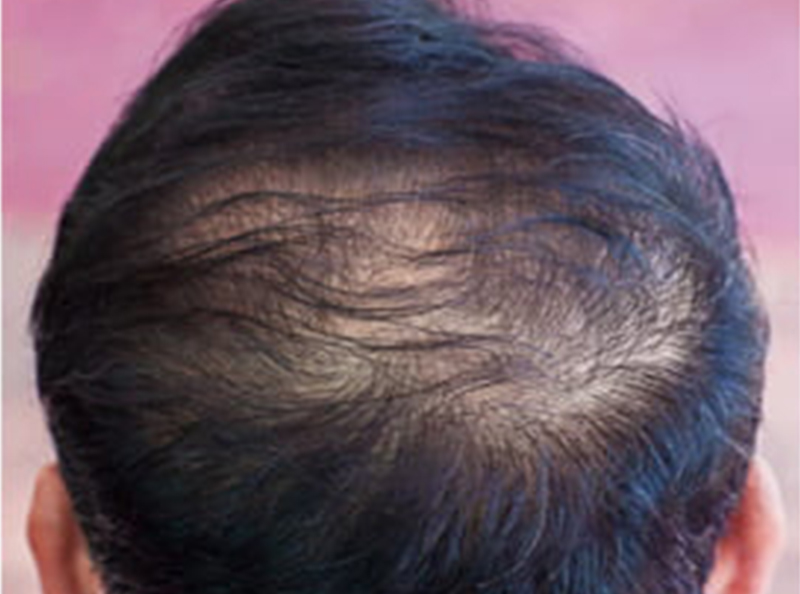
Telogen effluvium is a temporary form of hair loss characterized by a significant shedding of hair due to various factors, such as stress, illness, pregnancy, or certain medications. The hair follicles enter the resting phase prematurely, leading to excessive hair loss.
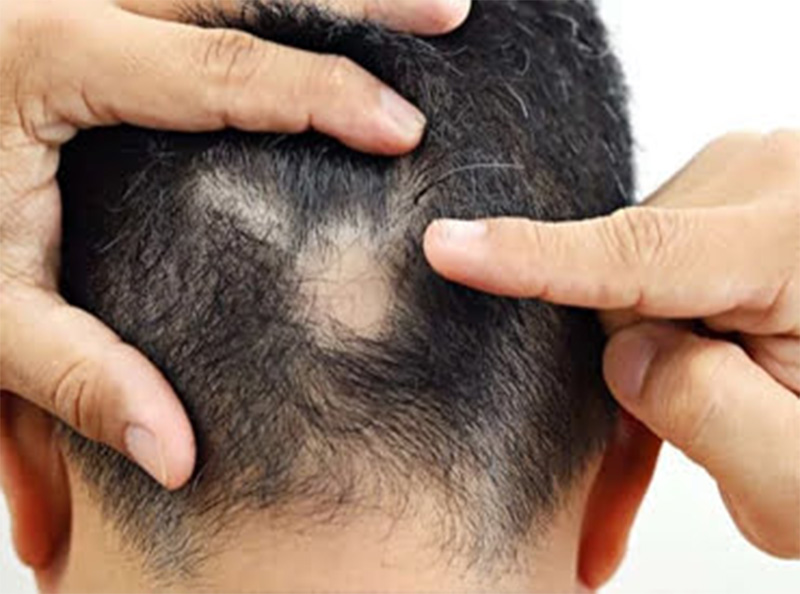
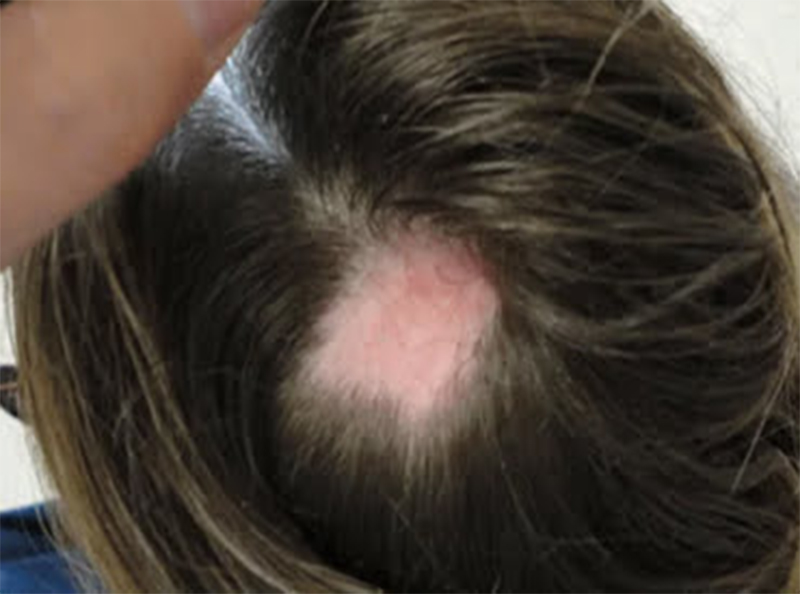
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that causes hair loss in patches. The immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, resulting in smooth, round areas of baldness on the scalp, face, or other parts of the body. This type of hair loss can be unpredictable and may resolve on its own or require treatment.
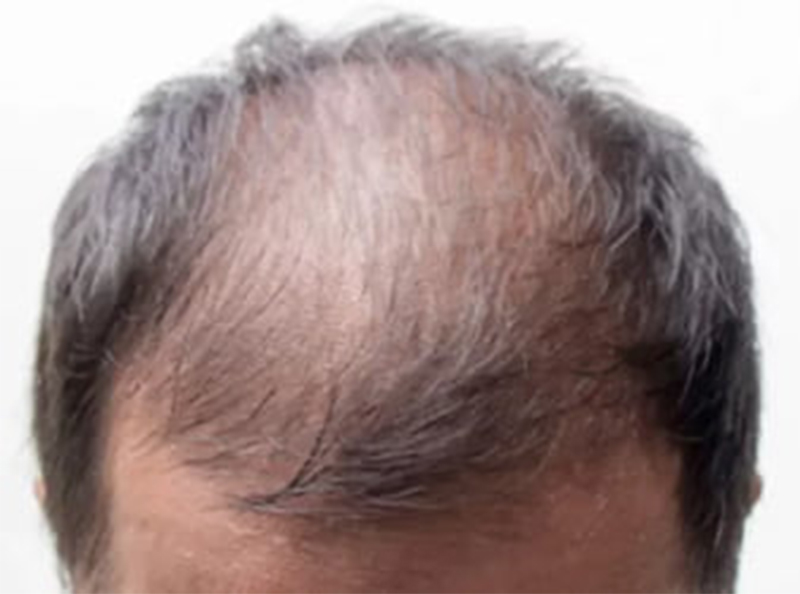
Traction alopecia occurs when there is excessive tension or pulling on the hair, often due to tight hairstyles like braids, ponytails, or extensions. Over time, this constant pulling can damage the hair follicles, leading to hair thinning and loss in the affected areas.
Cicatricial alopecia, also known as scarring alopecia, is a type of hair loss characterized by irreversible damage to the hair follicles, resulting in scar tissue formation. The scarred areas hinder hair regrowth, leading to permanent hair loss. Causes include inflammation, infections, or underlying medical conditions.
Genetics play a significant role in hair loss. If your family has a history of hair thinning or baldness, you may be genetically predisposed to experience similar concerns.
Hormonal changes, especially during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can trigger hair loss. Fluctuations in hormones can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to noticeable shedding.
Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, blood thinners, and antidepressants, can cause hair loss as a side effect. It’s crucial to consult your healthcare provider if you notice unusual hair thinning while taking any medications.
Various medical conditions like thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and alopecia areata can contribute to hair loss. Managing the underlying medical issue is crucial in addressing hair loss effectively.
Chronic stress can disrupt the natural hair growth cycle, leading to increased shedding and hair thinning. Implementing stress-reducing techniques and maintaining a balanced lifestyle can mitigate this effect.
A diet lacking essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and proteins can weaken hair and contribute to hair loss. Ensure your diet is rich in these vital elements to support healthy hair growth.
Deficiencies in specific vitamins and minerals, such as iron, zinc, and biotin, can directly impact hair health. Supplementing these nutrients or adjusting your diet accordingly can help combat hair loss.
Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle can adversely affect your hair health. Adopting a healthier lifestyle by quitting smoking, moderating alcohol intake, and staying physically active can aid in reducing hair loss.
