Diabetes Type 1
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing β (beta) cells in the pancreatic islets of Langerhans. This targeted destruction leads to an inflammatory response known as insulitis.
Over time, the pancreas of individuals with Type 1 diabetes typically becomes smaller, lighter, and shows abnormalities in blood vessels, nerve innervation, and extracellular matrix organization.
Without proper treatment blood glucose levels remain chronically elevated, a condition known as hyperglycemia.
Diabetes type 1 symptoms
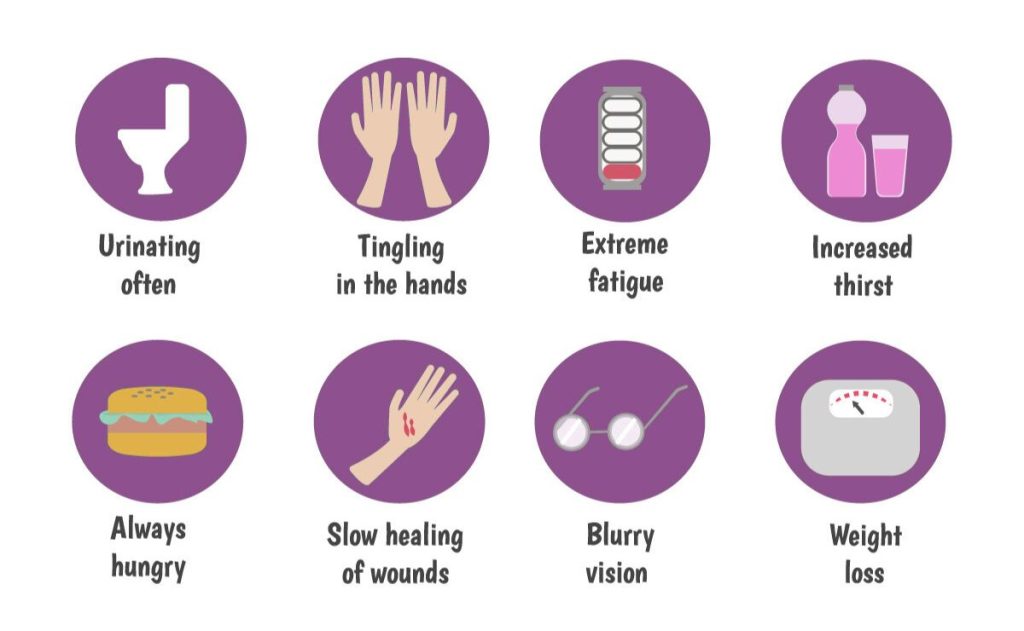
Diabetes type 1 risks

Book an Appointment Today
Contact Us
Phone number:
+91 6379926961
Location:
429A, V.V.C Layout, Pulliyakulam Road, Coimbatore – 641018.
Email:
support@namashivayah.com
Hand collected herbs from forests
*
100% organic
*
Diabetes type 1
*